Brainspotting to resolve unprocessed trauma
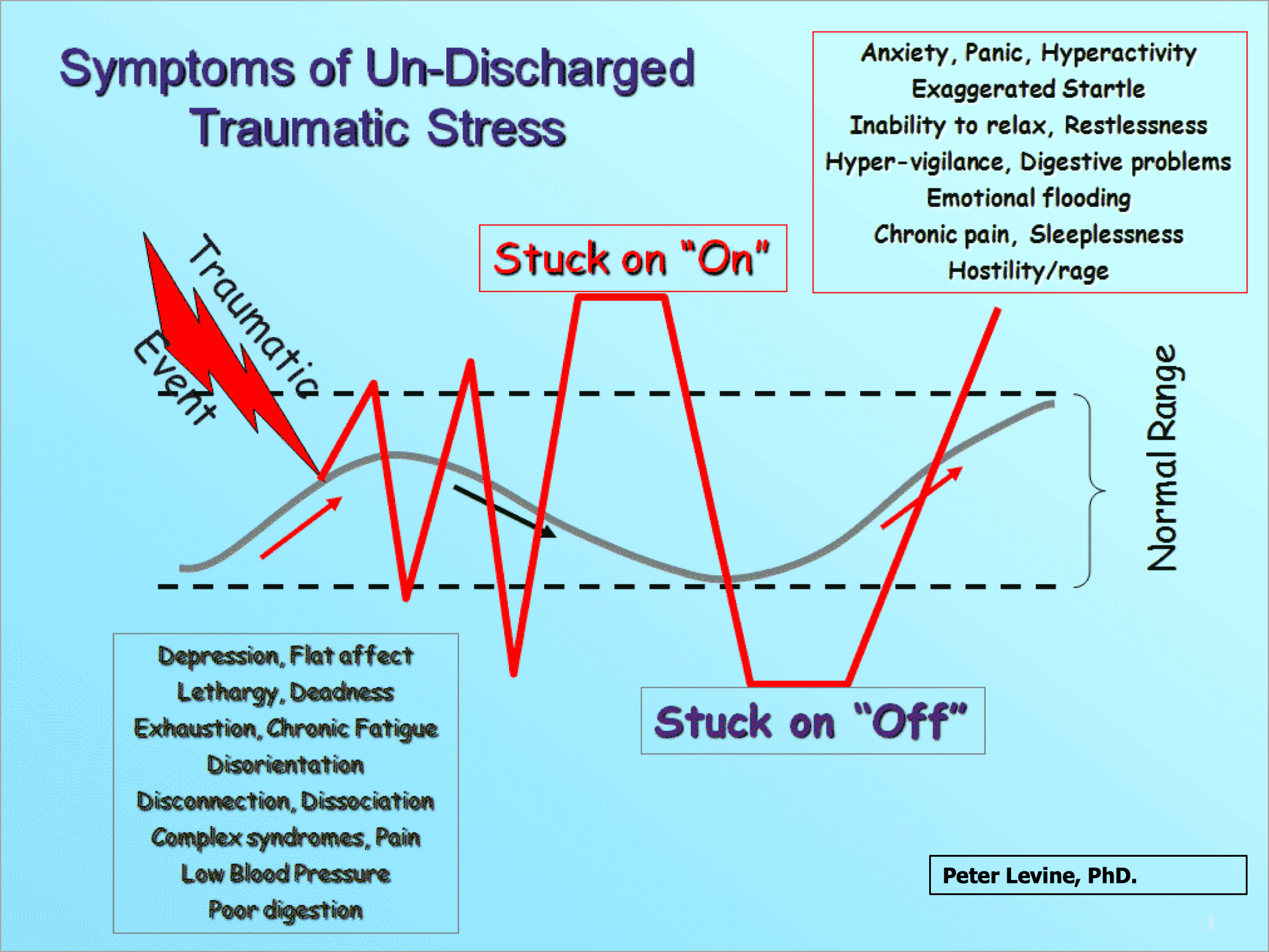
Brainspotting is a therapeutic approach that was developed by Dr. David Grand in 2003 and has grown in resources and effectiveness since then. It has gained popularity in the field of trauma therapy and has been found effective for various emotional and psychological issues.
“Where you look affects how you feel…If something is bothering you, how you feel about it will literally change depending on whether you look off to your right or to your left. Our eyes and brains are intricately woven together, and vision is the primary way that we, as humans, orient ourselves to our environment. Signals sent from our eyes are deeply processed in the brain.”
How Does Brainspotting Work?
1. The Brain-Body Connection: Brainspotting is based on the understanding that our brains and bodies are interconnected, and that our eye positions can help access and process unprocessed trauma, emotions, and memories in the brain. Traumatic or emotionally charged experiences can get stored in our nervous system, leading to emotional distress and physical symptoms. The central concept is that there are "brainspots" in our field of vision which are connected to specific emotional or physiological experiences. These spots are activated when we focus our gaze on them.
2. The Visual System: Brainspotting recognizes the relationship between our visual system and our brain's processing of emotions and memories. The human brain has a vast network of connections between the visual cortex (responsible for processing visual information) and the limbic and subcortical systems (involved in regulating emotions, memory, and their somatic manifestations). It draws on the concept that specific eye positions can activate different neural networks and access deep emotional and traumatic material.
3. Identification of Brainspots: In a Brainspotting session, the practitioner helps you identify what are known as "brainspots." These are specific points in your visual field that are associated with your emotional or traumatic experiences, corresponding to a specific issue, trauma, or emotion. These spots are linked to the activation of subcortical neural networks related to those experiences.
4. Focused Attention: The practitioner guides you in maintaining focused attention on the brainspot while simultaneously being aware of your bodily sensations, thoughts, and emotions. This sustained focus allows for deep processing of the stored trauma or emotional distress.
5. Dual Attunement: One of the unique aspects of Brainspotting is the concept of "dual attunement." This means that both you and the practitioner are attuned to your inner experiences during the session. The practitioner observes your non-verbal cues and helps you navigate your emotions without requiring you to verbally describe them (you are free to remain silent or express whatever you wish).
6. Processing and Integration: As you maintain your focus on the brainspot, your brain is activated to process and integrate the traumatic or distressing memories, emotions, and sensations. This can lead to the release of stored tension, new insights, and a reduction in emotional distress. Brainspotting aims to promote the integration of these experiences into your psyche, fostering healing and growth.
The exact neurological mechanisms at play are still the subject of ongoing research. The field of neuropsychology is continually advancing, and our understanding of how therapies like Brainspotting affect the brain may become clearer with further research and exploration.
Benefits of Brainspotting
1. Effective for Trauma: Brainspotting has been particularly effective in treating trauma-related issues, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), without requiring detailed verbal recounting of traumatic events.
2. Neuroplasticity: change from Brainspotting is based on the concept of neuroplasticity, which is the brain's ability to reorganize and form new neural connections throughout a person's life. The therapeutic process is believed to tap into this capacity for change by helping the brain reprocess and reframe traumatic or emotionally charged experiences through the identified brainspot, by which the brain may gradually reorganize itself, leading to symptom relief and emotional healing.
3. Deep Emotional Processing: Brainspotting can access and process emotions and memories that may be difficult to reach through traditional talk therapy because unprocessed trauma is ‘stored’ at the subcortical level, deeper than the verbal cerebral level. It allows for a deeper activation of subconscious material and allows access to early, preverbal phenomena. It taps into the brain's natural healing mechanisms.
4. Reduction in Symptoms: Many patients report a significant reduction in symptoms like anxiety, depression, and PTSD after Brainspotting sessions.
5. Reduced Re-traumatization: Because it doesn't require you to verbalize traumatic experiences, it can be less re-traumatizing compared to some other therapies.
6. Faster Results: Some individuals have reported quicker and more lasting results with Brainspotting than with traditional talk therapy, which may take longer to uncover and address underlying issues.
7. Individualized Approach: Brainspotting is highly individualized, adapting to your unique experiences and needs. The practitioner maintains a discipline of refraining from imposing interpretations or analyses.